Restorative yoga is a gentle, calming practice designed to relax the body and mind, promoting deep healing and rejuvenation. While many restorative poses traditionally utilize props, it’s entirely possible to practice restorative yoga effectively without them. This article explores a variety of restorative yoga postures that can be performed without props, providing detailed instructions, benefits, and sequences to enhance relaxation and well-being.
Understanding Restorative Yoga
What is Restorative Yoga?
Restorative yoga is a practice that emphasizes relaxation and stress relief. It involves holding poses for extended periods—often five minutes or more—to encourage deep release and restoration. The focus is on gentle stretching and breathing, allowing practitioners to experience a profound sense of calm.
Benefits of Restorative Yoga
The benefits of restorative yoga are numerous and can include:
Stress Reduction: Helps calm the nervous system and reduce anxiety.
Improved Flexibility: Encourages gentle stretching, enhancing overall flexibility.
Increased Mindfulness: Promotes present-moment awareness through focused breathing and relaxation.
Enhanced Recovery: Aids in physical recovery from workouts or injury.
The Importance of Breath in Restorative Yoga
The Breath Connection
Breath plays a crucial role in restorative yoga. Slow, deep breaths can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and healing. Practicing mindful breathing enhances the benefits of each pose.
Breathing Techniques
Diaphragmatic Breathing: Focus on breathing deeply into the diaphragm, allowing the abdomen to rise and fall with each breath.
Extended Exhalation: Inhale for a count of four, then exhale for a count of six or eight to promote relaxation.
Ujjayi Breath: A soft constriction of the throat creates a soothing sound, enhancing focus and calming the mind.
Restorative Postures Without Props
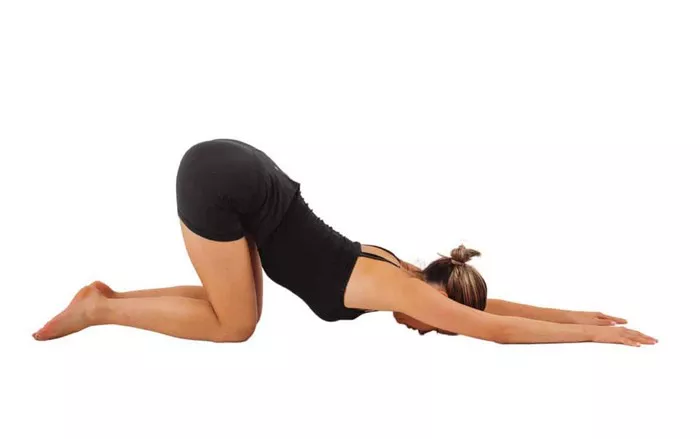
1. Child’s Pose (Balasana)
Instructions:
Kneel on the floor, bringing your big toes together and sitting back on your heels.
Extend your arms forward or let them rest alongside your body.
Relax your forehead on the mat and breathe deeply.
Benefits:
Calms the mind and relieves stress.
Stretches the hips, thighs, and spine.
2. Legs-Up-The-Wall Pose (Viparita Karani)
Instructions:
Lie on your back and extend your legs up the wall.
Keep your arms relaxed at your sides or rest them on your belly.
Focus on deepening your breath.
Benefits:
Improves circulation and reduces fatigue.
Calms the nervous system and alleviates anxiety.
3. Supine Bound Angle Pose (Supta Baddha Konasana)
Instructions:
Lie on your back and bring the soles of your feet together, allowing your knees to fall open.
Place your hands on your belly or by your sides.
Breathe deeply and relax.
Benefits:
Opens the hips and promotes relaxation.
Reduces tension in the lower back.
4. Seated Forward Bend (Paschimottanasana)
Instructions:
Sit with your legs extended straight in front of you.
Inhale and lengthen your spine, then exhale as you hinge at the hips to fold forward.
Allow your hands to rest on your legs or the floor.
Benefits:
Calms the mind and relieves anxiety.
Stretches the spine and hamstrings.
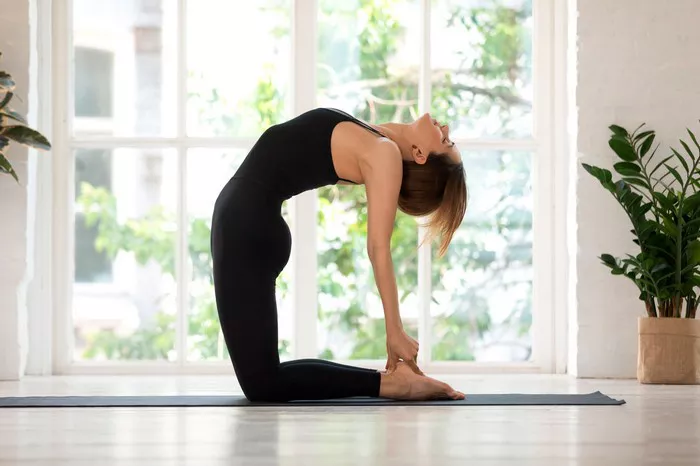
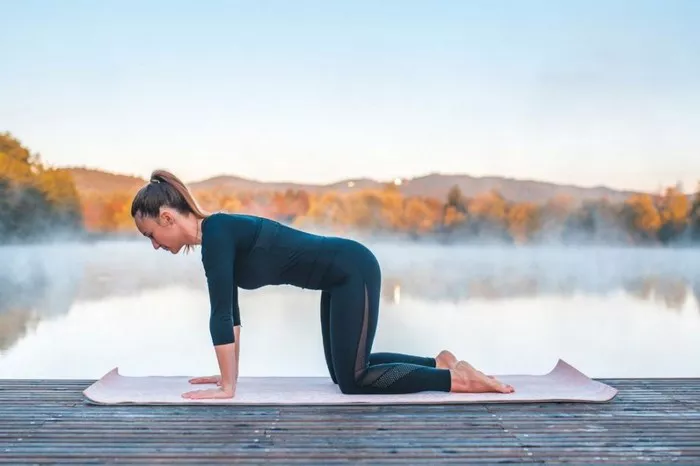
5. Cat-Cow Pose (Marjaryasana-Bitilasana)
Instructions:
Begin on all fours with your wrists under your shoulders and knees under your hips.
Inhale as you arch your back (Cow Pose), and exhale as you round your spine (Cat Pose).
Flow gently between the two poses.
Benefits:
Increases spinal flexibility and relieves tension.
Promotes breath awareness and mindfulness.
6. Supine Spinal Twist (Supta Matsyendrasana)
Instructions:
Lie on your back and bring your knees to your chest.
Allow your knees to fall to one side while keeping your shoulders on the ground.
Extend your arms out to the sides for support.
Benefits:
Relieves tension in the spine and promotes relaxation.
Aids digestion and detoxification.
7. Bridge Pose (Setu Bandhasana)
Instructions:
Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet hip-width apart.
Press your feet into the ground and lift your hips toward the ceiling.
Keep your arms at your sides, breathing deeply.
Benefits:
Opens the chest and stretches the spine.
Strengthens the legs and promotes circulation.
8. Corpse Pose (Savasana)
Instructions:
Lie flat on your back with your arms at your sides, palms facing up.
Allow your feet to fall naturally outward.
Close your eyes and focus on your breath.
Benefits:
Promotes deep relaxation and stress relief.
Enhances mindfulness and body awareness.
See also: Restorative Yoga for Beginners: Relaxation and Healing
Creating a Restorative Yoga Sequence Without Props
Sample Sequence for Relaxation
Child’s Pose (5 minutes)
Legs-Up-The-Wall Pose (5 minutes)
Supine Bound Angle Pose (5 minutes)
Seated Forward Bend (5 minutes)
Cat-Cow Pose (5 minutes)
Supine Spinal Twist (5 minutes each side)
Bridge Pose (5 minutes)
Corpse Pose (10 minutes)
Tips for Sequencing
Focus on Breath: Allow each pose to flow into the next, using breath as your guide.
Hold Poses Longer: Extend the duration of each pose to deepen relaxation.
Listen to Your Body: Modify or skip poses based on your comfort level.
Tips for Practicing Restorative Yoga Without Props
Creating the Right Environment
Quiet Space: Find a peaceful location free from distractions.
Soft Lighting: Dim the lights or use candles to create a calming atmosphere.
Comfortable Clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothes that allow for easy movement.
Mindfulness and Intention
Set an Intention: Begin your practice by setting a personal intention, whether it’s relaxation, stress relief, or healing.
Stay Present: Focus on your breath and sensations in your body, allowing thoughts to come and go without attachment.
Integrating Restorative Yoga into Daily Life
Short Practices: Incorporate brief restorative sessions into your daily routine, even if just for 10-15 minutes.
Combine with Other Practices: Pair restorative yoga with other forms of exercise or mindfulness practices to enhance overall well-being.
The Impact of Restorative Yoga on Mental Health
Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Restorative yoga has been shown to effectively reduce stress and anxiety levels. By promoting relaxation, it helps lower cortisol levels, the stress hormone, leading to improved mental health.
Enhancing Emotional Well-being
The practice encourages emotional release and mindfulness, allowing individuals to process feelings and cultivate a sense of peace. This can be particularly beneficial for those dealing with depression or emotional challenges.
Building Resilience
Regular practice can foster resilience, helping individuals cope with life’s challenges more effectively. The mindfulness cultivated through restorative yoga can enhance self-awareness and emotional regulation.
Conclusion
The Healing Power of Restorative Yoga
Restorative yoga postures without props offer a valuable way to achieve relaxation, stress relief, and overall well-being. By focusing on breath and gentle movements, practitioners can experience profound benefits without the need for additional equipment.
Embracing the Practice
As you explore these restorative postures, remember that the journey is personal. Take the time to listen to your body and adapt the practice to suit your needs. With consistency and mindfulness, restorative yoga can become a cherished tool for nurturing your body and mind.
Final Thoughts
Incorporating restorative yoga into your life can lead to significant improvements in both physical and mental health. Embrace the calming effects of these postures and discover the transformative power of rest and relaxation.
You Might Be Interested In
Warm Restorative Yoga: A Guide to Deep Relaxation and Healing
What is Full Moon Restorative Yoga Sequence
How to Do Restorative Yoga with A Chair: A Comprehensive Guide